Top 10 Cited Papers
TOP 10 Computer Networks & Communications Research Articles
TOP 1
DELAY-POWER PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF MULTIPLIERS IN VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN
Sumit Vaidya1 and Deepak Dandekar2
1Department of Electronic & Telecommunication Engineering, OM College of Engineering, Wardha, Maharashtra, India
2Department of Electronic Engineering, B. D. College of Engineering, Wardha, Maharashtra, India
ABSTRACT:
A typical processor central processing unit devotes a considerable amount of processing time in performing arithmetic operations, particularly multiplication operations. Multiplication is one of the basic arithmetic operations and it requires substantially more hardware resources and processing time than addition and subtraction. In fact, 8.72% of all the instruction in typical processing units is multiplication. In this paper, comparative study of different multipliers is done for low power requirement and high speed. The paper gives information of “Urdhva Tiryakbhyam” algorithm of Ancient Indian Vedic Mathematics which is utilized for multiplication to improve the speed, area parameters of multipliers. Vedic Mathematics suggests one more formula for multiplication of large number i.e. “Nikhilam Sutra” which can increase the speed of multiplier by reducing the number of iterations.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0710ijcnc05.pdf
TOP 2
UBIQUITOUS SMART HOME SYSTEM USING ANDROID APPLICATION
Shiu Kumar
Department of Information Electronics Engineering, Mokpo National University, 534-729, Mokpo, South Korea
ABSTRACT:
This paper presents a flexible stand-alone, low-cost smart home system, which is based on the Android app communicating with the micro-web server providing more than the switching functionalities. The Arduino Ethernet is used to eliminate the use of a personal computer (PC) keeping the cost of the overall system to a minimum while voice activation is incorporated for switching functionalities. Devices such as light switches, power plugs, temperature sensors, humidity sensors, current sensors, intrusion detection sensors, smoke/gas sensors and sirens have been integrated into the system to demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed smart home system. The smart home app is tested and it is able successfully to perform the smart home operations such as switching functionalities, automatic environmental control, and intrusion detection, in the latter case where an email is generated and the siren goes on.
Full Article: http://www.airccse.org/journal/cnc/6114cnc03.pdf



TOP 3
OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF READERS IN AN RFID NETWORK USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION
Indrajit Bhattacharya1, Uttam Kumar Roy2
1 Kalyani Govt. Engg. College, Kalyani, Nadia, India
2Dept. of IT, Jadavpur University, Kolkata-700098, India
ABSTRACT:.
An RFID network consists of a set of tags and readers. The cost and the number of tags covered directly depend on the number of readers. So, finding optimal number of readers and their positions to cover all tags is one of the most important issues in an RFID network. In this paper, we have proposed a reader placement technique in a departmental store equipped with RFID network using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). The proposed algorithm finds minimal number of readers along with their position with 100% coverage of tagged items. Simulated results also show the algorithms effectiveness in achieving the optimal solution.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/1110ijcnc15.pdf



TOP 4
TOWARDS INTERNET OF THINGS (IOTS): INTEGRATION OF WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK TO CLOUD SERVICES FOR DATA COLLECTION AND SHARING
Rajeev Piyare1 and Seong Ro Lee2
1,2Department of Information Electronics Engineering, Mokpo National University, 534- 729, South Korea
ABSTRACT:
Cloud computing provides great benefits for applications hosted on the Web that also have special computational and storage requirements. This paper proposes an extensible and flexible architecture for integrating Wireless Sensor Networks with the Cloud. We have used REST based Web services as an interoperable application layer that can be directly integrated into other application domains for remote monitoring such as e-health care services, smart homes, or even vehicular area networks (VAN). For proof of concept, we have implemented a REST based Web services on an IP based low power WSN test bed, which enables data access from anywhere. The alert feature has also been implemented to notify users via email or tweets for monitoring data when they exceed values and events of interest.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/5513cnc05.pdf


TOP 5
IMPACT OF MOBILITY MODELS ON MULTI-PATH ROUTING IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Nicholas Cooper 1 and Natarajan Meghanathan 2
1Northern Kentucky University, Nunn Drive, Highland Heights, KY, USA
2 Jackson State University, 1400 Lynch St, Jackson, MS, USA
ABSTRACT:
The high-level contribution of this paper is a detailed simulation-based analysis about the impact of mobility models on the performance of node-disjoint and link-disjoint multi-path routing algorithms for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs). We consider the following MANET mobility models: Random Waypoint, Random Direction, Gauss-Markov, City Section and Manhattan mobility models. Simulations have been conducted for various network density and node mobility levels. The performance metrics studied include the lifetime per multi-path set, the multi-path set size and the average hop count per multi-path. For almost every simulation condition, we observe the Gauss-Markov mobility model to yield the least number of multi-paths, but the lifetime per multi-path set under this mobility model is the maximum. The Random Direction mobility model yields the smallest lifetime per multi-path set, even though it yields a relatively larger number of multi-paths.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0110s013.pdf



TOP 6
ANALYZING THE PERFORMANCE OF ACTIVE QUEUE MANAGEMENT ALGORITHMS
G.F.Ali Ahammed 1, Reshma Banu 2
1Department of Electronics & Communication, Ghousia college of Engg.Ramanagaram, India
2Department of Information Science & Engg, Ghousia college of Engg.Ramanagaram,India
ABSTRACT:
Congestion is an important issue which researchers focus on in the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) network environment. To keep the stability of the whole network, congestion control algorithms have been extensively studied. Queue management method employed by the routers is one of the important issues in the congestion control study. Active queue management (AQM) has been proposed as a router-based mechanism for early detection of congestion inside the network. In this paper, we analyzed several active queue management algorithms with respect to their abilities of maintaining high resource utilization, identifying and restricting disproportionate bandwidth usage, and their deployment complexity. We compare the performance of FRED, BLUE, SFB, and CHOKe based on simulation results, using RED and Drop Tail as the evaluation baseline. The characteristics of different algorithms are also discussed and compared. Simulation is done by using Network Simulator(NS2) and the graphs are drawn using X- graph.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/10101.pdf


TOP 7
ANOMALY INTRUSION DETECTION DESIGN USING HYBRID OF UNSUPERVISED AND SUPERVISED NEURAL NETWORK
M. Bahrololum, E. Salahi and M. Khaleghi
IT Security and Systems Group Iran Telecommunication Research Center, Tehran, Iran
ABSTRACT:
This paper proposed a new approach to design the system using a hybrid of misuse and anomaly detection for training of normal and attack packets respectively. The utilized method for attack training is the combination of unsupervised and supervised Neural Network (NN) for Intrusion Detection System. By the unsupervised NN based on Self Organizing Map (SOM), attacks will be classified into smaller categories considering their similar features, and then unsupervised NN based on Backpropagation will be used for clustering. By misuse approach known packets would be identified fast and unknown attacks will be able to detect by this method.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0709s03.pdf

TOP 8
TRUST BASED CLUSTERING AND SECURE ROUTING SCHEME FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Pushpita Chatterjee
School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, India
ABSTRACT:
In this paper we present a distributed self-organizing trust based clustering framework for securing ad hoc networks. The mobile nodes are vulnerable to security attacks, so ensuring the security of the network is essential. To enhance security, it is important to evaluate the trustworthiness of nodes without depending on central authorities. In our proposal the evidence of trustworthiness is captured in an efficient manner and from broader perspectives including direct interactions with neighbors, observing interactions of neighbors and through recommendations. Our prediction scheme uses a trust evaluation algorithm at each node to calculate the direct trust rating normalized as a fuzzy value between zero and one. The evidence theory of Dempster-Shafer [7], [8] used in order to combine the evidences collected by a clusterhead itself and the recommendations from other neighbor nodes. Moreover, in our scheme we do not restrict to a single gateway node for inter cluster routing.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0709s08.pdf


TOP 9
NETWORK MOBILITY SUPPORT SCHEME ON PMIPV6 NETWORKS
Hyo-Beom Lee1,Youn-HeeHan2 and Sung-Gi Min1
1Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea.
2 School of Internet-Media, Korea University of Technology and Education, Cheon-An, South Korea.
ABSTRACT:
NEMO (Network Mobility) is proposed to support node mobility collectively. NEMO BSP is the most popular protocols to support NEMO based on MIPv6. However, it does not satisfy requirements of realtime and interactive application due to problems, such as long signaling delay and movement detection time. Also, MN should have mobility function for its handover. Proxy MIPv6 (PMIPv6) is proposed to overcome defects of MIPv6 based protocols. In this paper, we propose a Network Mobility supporting scheme, which supports MNs’ mobility between PMIPv6 network and mobile network as well as the basic network mobility.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0910ijcnc13.pdf

TOP 10
USING DSR FOR ROUTING MULTIMEDIA TRAFFIC IN MANETS
Ronald Beaubrun and Badji Molo
Department of Computer sciences and software engineering Laval University, Canada
ABSTRACT:
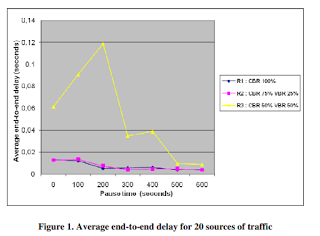
In mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs), links are created and destroyed in an unpredictable way, which makes quite challenging the determination of routes between each pair of nodes. In this paper, we propose a formulation of the routing problem in multi-services MANETs, as well as the implementation of an adaptation of the dynamic source routing (DSR) protocol. Simulation results reveal that DSR enables to provide end-to-end delay less than 0.11 s, as well as packet delivery ratio higher than 99% and normalized routing load less than 13%, for low mobility level and low traffic intensity.
Full Article: http://airccse.org/journal/cnc/0110s09.pdf





Recent Comments